Selecting The Top Parent
What is a Top Parent?
Each IntraVUE™ 'network' is a grouping of logical devices depending on the needs of the user. Each IntraVUE™ network consists of a set of scan ranges and a Top Parent.
Only two devices can be a top parent: the host computer and a router (layer 3 switch) for which the snmp community is known.
Definitions:
The Top Parent of an IntraVUE™ network is the device which can provide the MAC addresses for the devices in the scan range.
Local: all devices in the same subnet as the IntraVUE™ host ip address.
Local is determined by applying the IP address of a computer to its subnet mask. Pings to local ip addresses will go directly to the device and the MAC will be stored in the host computer's ARP cache.
An online subnet calculator is useful if you have unusual subnet masks. www.subnetonline.com and www.subnetmask.info are two examples.
Remote: all devices NOT in the same subnet as the IntraVUE™ host ip address. Pings and other traffic to remote devices will leave the local subnet and go to the default gateway (a router) if one is configured. The gateway will use its routing tables to direct the traffic to one of its interfaces or its gateway if it does not have an appropriate interface.
General rules for determining the ‘top parent’:
The IntraVUE™ host computer must be the top parent if any devices in an IntraVUE™ network are local to the host. This is because the MAC addresses will be in the host's ARP cache as a result of the scanner's pings.
The MAC addresses for any devices not 'local' to the IntraVUE™ host computer will be in a router. They will be in the last router leading to a device, the so-called 'last hop router'. Generally, the gateway IP address of a remote subnet is the correct top parent for that subnet.
A router only needs to be in one IntraVUE™ network to find the MAC addresses for all other IntraVUE™ networks. Putting the router in its own IntraVUE™ network with no other devices is one method of doing this.
The IP address of a network’s top parent must be included in one of the IP address ranges for that network.
Again, the top parent of each IntraVUE™ network is the device which has access to the MAC address information on the devices that will be in its scan range(s).
A very detailed document covering the configuration of many types of networks, from very simple to very complex is at How To Configure IntraVUE™ networks
The scanner will attempt to identify any routers that are in a scan range and the scanner will try to get additional MAC addresses from any router it finds.
If an IntraVUE™ network has some devices that are local and some devices that are remote, the host computer must be the top parent and one (and only one) of the router's ip addresses should be in a scan range.
If you have VLAN's each VLAN should be in a separate IntraVUE™ network. This will result in clearly showing the path traffic takes to go from one device to another.
If switches are in a separate VLAN, that IP address range can be added to each other VLAN's scan ranges. Thus, each IntraVUE™ network will have the switches and show how devices are connected. Switches that are not used in a particular VLAN can later be deleted from that IntraVUE™ network.
Example:
If there is one router and many VLANS and you want to scan those VLANs, make the interface (IP) of the router of that VLAN the top parent for that VLAN. This will make it easier to navigate the browser when there are many VLANs or networks.
IntraVUE™ host is 10.1.1.35.
Router has IP addresses 10.1.1.1, 10.1.2.1, 10.1.3.1, and 192.168.1.254.
You want to scan all those class C ranges.
Network 1
top parent 10.1.1.35 (local host to get MACs of local devices)
range 10.1.1.0 - 10.1.1.255 (includes the router 10.1.1.1 and top parent)
Network 2
top parent 10.1.2.1
range 10.1.2.1 - 10.1.2.255
Network 3
top parent 10.1.3.1
range 10.1.3.1 - 10.1.3.255
Network 4
top parent 192.168.1.254
range 192.168.1.1 - 192.168.1.254
IF YOU ARE SCANNING ANY DEVICES LOCAL TO THE HOST COMPUTER, the host is the ONLY device which can be the top parent. This is because only the host will have the MAC addresses for the local devices which the scanner is pinging. (While the gateway router may know some of the MACs it will only know the ones that communicate outside the local subnet.
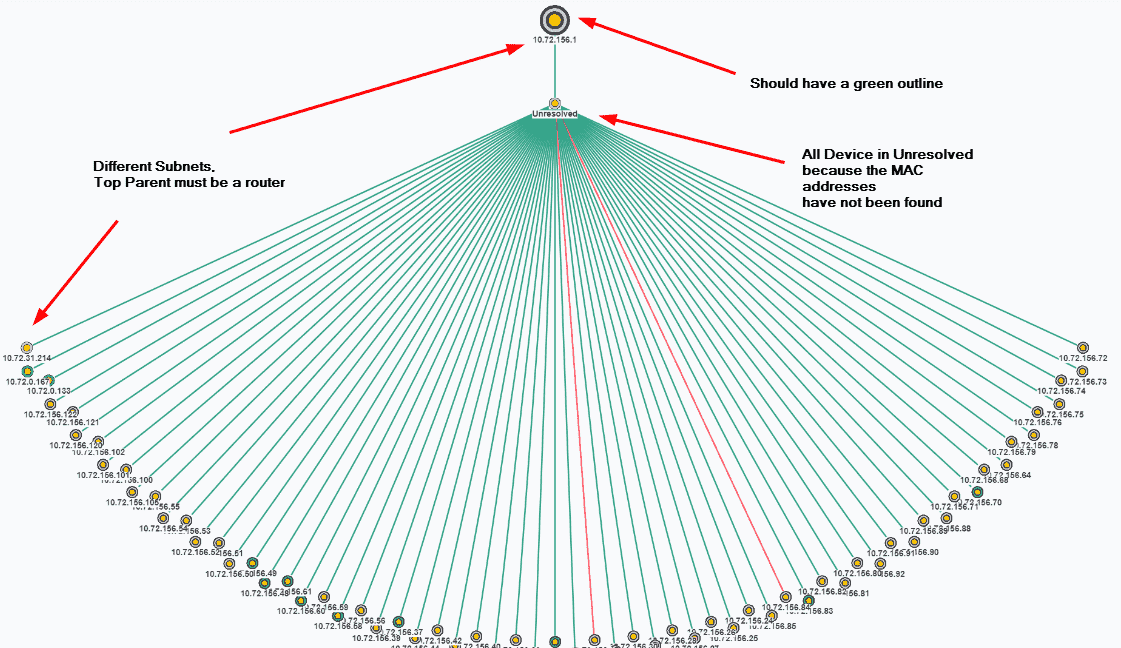
If you do not select the correct top parent, or the top parent is not configured to successfully use SNMP, you will see something like the image below in your browser.
If the top parent is not the local computer, it must be a router because routers are devices that tell mac addresses when provided an IP address. In the image, the top parent is in an IP address range separate from the devices that are scanned. That is a clue that the top parent must be a router.
In the image, there is no green outline surrounding the top parent node. If the IP of the top parent IS a router, then the SNMP community is not correct or the router has been configured with an Access Control List and the IntraVUE™ host is not on the list.
If the top parent is not the local computer, it must have a green outline indicating there is succssful SNMP communication with the ROUTER that knows the MAC addresses of the devices in the scan range.
See also Configure Menu - Scanner Tab, and Completing Initial Configuration.
